Volume 45 Number 3 (2014.9)
Special Feature
Drivetrain and Braking Technology
Part I. Special Feature
Overview
Research Reports
-
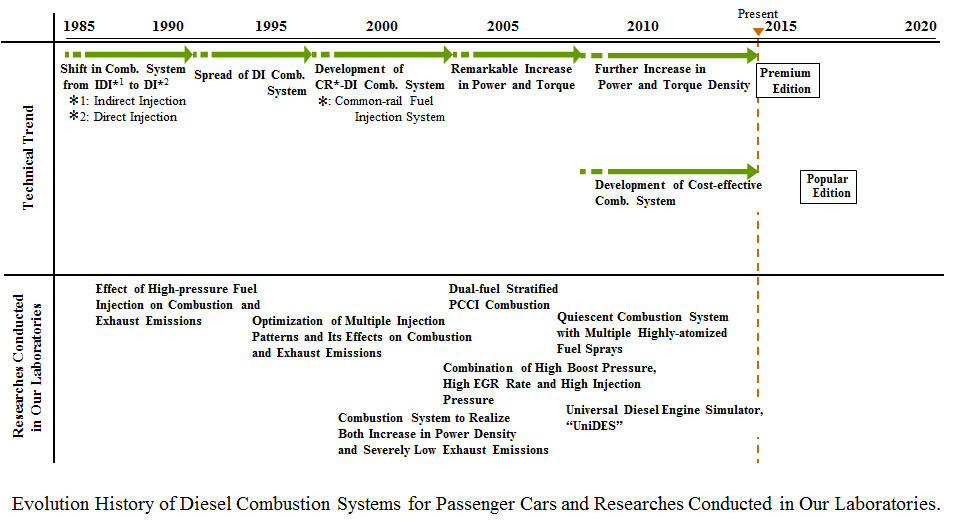
2. Robust Design Method for Automatic Transmission Clutch Control System
 (2,908kB)
(2,908kB)pages 1-11
Ryoichi Hibino, Tomohiro Miyabe, Masataka Osawa, Katsumi Kono and Hideaki Otsubo
In automatic transmissions, there are various disturbances such as clutch friction coefficient variations and oil temperature changes. Therefore, the system must be resistant to disturbances. In this study, design methods are proposed for robust control systems. The methods are applied to feedback and feedforward control systems widely used in transmissions.
-
pages 13-21
Kisaburo Hayakawa, Ryoichi Hibino, Masataka Osawa, Toshinori Murahashi, Naoki Koshi and Hiroaki Kato
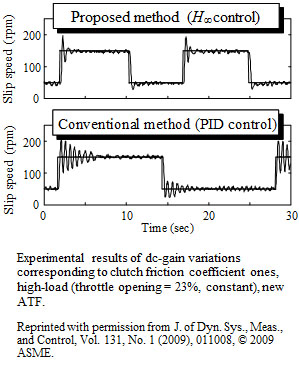
Vehicle weight was estimated by the original method which removes the influence of road gradient from the measured signals based on the difference of frequency characteristic. Vehicle experimental results showed that this method derives high accuracy of an estimation and good performance of an engine break control.
-
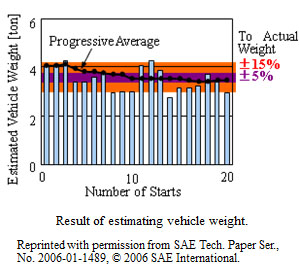
4. Measurement of the Behavior of a Metal V-belt for CVTs
 (1,795kB)
(1,795kB)pages 23-30
Hirofumi Tani, Hiroyuki Yamaguchi, Haruhiro Hattori, Masanori Shimizu, Kazuya Arakawa and
Yuji Hattori
We have developed a device that can measure the behavior of a metal V-belt in a continuously variable transmission (CVT). Variations in the inclination angle of the belt elements through one rotation of the belt were clarified and it was found to be necessary to reduce the element yaw angle in the primary pulley, especially for the lowest speed ratio, in order to increase the torque capacity of the CVT.
-
pages 31-42
Yoshitsugu Goto, Yuji Nagasawa and Toru Matsushima
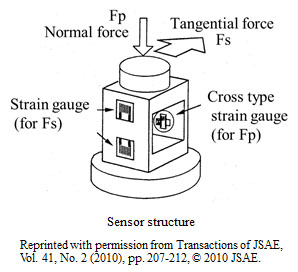
The contact condition of friction surfaces has a significant influence on brake squeal. Therefore, in the present study, we examine technology for measuring the distribution of normal pressure and friction forces between a disk rotor and brake pads and for optimizing contact surfaces through sensitivity analysis.
Part II.
Special Review
-
pages 43-56
Kiyomi Nakakita
Since 1990’s, high-speed direct-injection diesel engines for passenger cars have been making great strides through several stages in all of power, exhaust emissions, noise and vibration etc. At each stage, our laboratories played some key roles in clarifying in-cylinder phenomena and indicating directions and measures for improvement, which are introduced in this review.
Research Reports
-
7. Memory Effect in a Lithium-ion Battery
 (2,912kB)
(2,912kB)pages 57-67
Tsuyoshi Sasaki, Yoshio Ukyo and Petr Novák
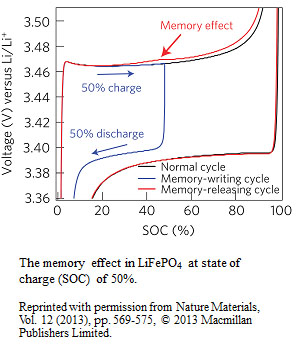
Until now, lithium-ion batteries have been widely believed to exhibit no memory effects. Here we report a memory effect in LiFePO4—one of the materials used for the positive electrode in Li-ion batteries. We characterize this memory effect and explain the mechanism. It is essential to understand and predict this phenomenon, in order to precisely estimate the SOC, and ensure the safe and effective use of lithium-ion batteries.
Brief Reports
-
8. Drowsy Driving Detection Based on Steering Maneuvers
 (610kB)
(610kB)pages 69-71
Tomoki Nishi, Pongtep Angkititrakul, Hiroyuki Yoshida, Yasuo Sakaguchi, Ryuta Terashima and Toshiki Ezoe
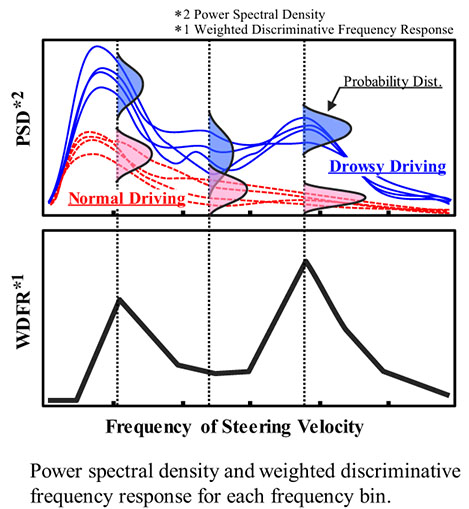
We have developed a drowsy driving detection method based on a filter with weighted discriminative frequency response, which is proportional to the Kullback-Leibler divergence between two probability distributions of power spectral density of steering velocity for the drowsy and normal states. The equal error rate of the proposed method was 8% lower than that of the conventional method.
-
9. Atomization Method Using Fuel/Cavitation Bubble Mixture Injection
 (546kB)
(546kB)pages 73-75
Ryo Masuda, Kiyomi Kawamura and Makoto Nagaoka
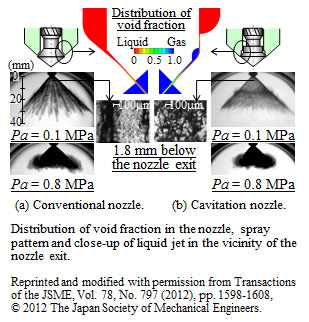
A liquid fuel injection nozzle with a novel fuel atomization strategy that utilizes the effect of collapse of cavitation bubbles in a liquid jet was proposed and investigated. The present nozzle achieves smaller droplet size and lower spray tip penetration than conventional nozzles.
-
10. WiFi Localization Method Using a Gaussian Process Particle Filter
 (719kB)
(719kB)pages 77-79
Seigo Ito
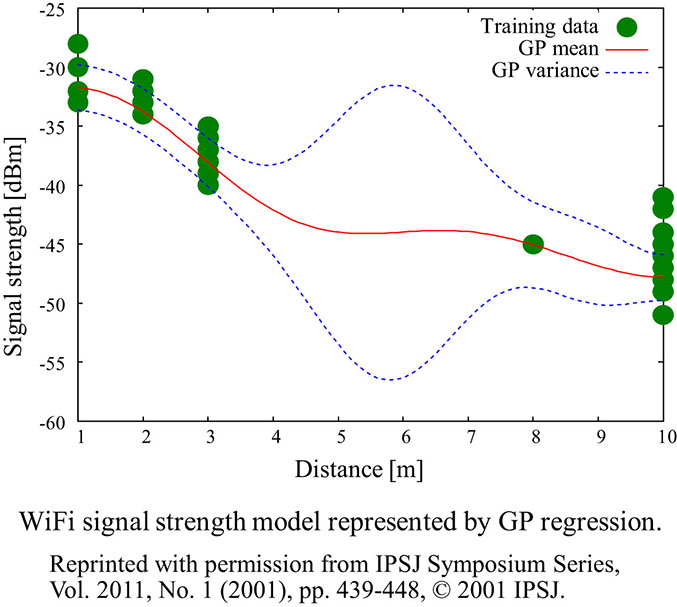
In the present paper, we address WiFi-based localization problems using the Gaussian process and a Gaussian process particle filter. Gaussian process regression takes into account the presence of training data and estimates the uncertainty of models. In addition, the uncertainty of the Gaussian process particle filter automatically increases when the target enters an area in which there is insufficient training data.