Mesoporous SnO2 catalyst supports for fuel cells improving its performance and durability
A study conducted by Masanori Inaba et al., in collaboration with Toyota Motor Corporation was published in the ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
In recent years, the focus of polymer electrolyte fuel cell application in automobiles has been shifting from light-duty vehicles to heavy-duty vehicles, which demand high durability, energy-conversion efficiency, and power density. While it is known that employing mesoporous carbons as catalyst supports enhances the initial performance of fuel cells, the carbon materials in the cathode can degrade oxidatively during long-term operation, requiring more stable materials.
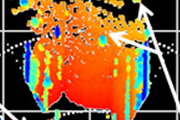
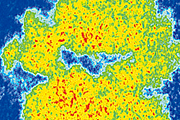
In this study, we synthesized mesoporous SnO2 particles with controlled mesopore sizes, and tested their performance and durability as cathode catalyst supports. It is demonstrated that employing a mesoporous SnO2 catalyst support with an appropriate pore size effectively improves both the performance and durability of the catalyst support. The insights obtained from this study are expected to contribute as guidelines for catalyst material development, further facilitating the widespread use of fuel cells.
Title: Synthesis of a Mesoporous SnO2 Catalyst Support and the Effect of Its Pore Size on the Performance of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells
Authors: Inaba, M., Murase, R., Takeshita, T., Yano, K., Kosaka, S., Takahashi, N., Isomura, N., Oh-ishi, K., Yoshimune, W., Tsuchiya, K., Nobukawa, T., Kodama, K.
Journal Name: ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
Published: February 21, 2024
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.4c01794