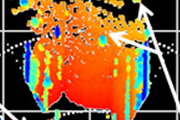
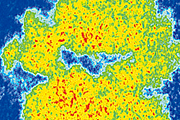
Improving the catalytic activity of cobalt-based oxides for water electrolyzers by surface functionalization
A study conducted by our researcher Wataru Yoshimune at Paul Scherrer Institute was published in the Small Structures.
Water electrolyzers are a promising electrochemical energy conversion device for producing green hydrogen from intermittent renewable energy sources. Alkaline exchange membrane water electrolyzers (AEMWEs) can use various non-noble metal oxides as anode catalysts, potentially overcoming the problem of cost reduction. In AEMWEs, catalytic activity over a wide pH range is important for practical applications. This study investigates a surface functionalization method to improve the catalytic activity of cobalt-based oxides. We disclose that phosphate ion functionalization on the oxide surface is effective in improving the catalytic activity, and that the surface modification is more effective in a cobalt-based catalyst without electrochemically inactive surface segregation layers. Our findings provide a new guideline for the material design of highly active catalysts in AEMWEs.
Title: The Role of Phosphate Functionalization on the Oxygen Evolution Reaction Activity of Cobalt-based Oxides at Different pH Values
Authors: Yoshimune, W., Falqueto, JB., Clark, AH., Yüzbasi, NS., Graule, T., Baster, D., El Kazzi, M., Schmidt, TJ., Fabbri, E.
Journal Name: Small Structures
Published: Augast 31, 2023
https://doi.org/10.1002/sstr.202300106