Elucidation of the unique characteristics of yielding in glass arising from its random structure
A study conducted by Norihiro Oyama, in collaboration with Nagoya University, Osaka University and The University of Tokyo, was published in the Physical Review Letters.
Glass is known to be a state where a collection of particles solidifies without forming a crystalline structure. The material properties of crystalline solids can be predicted by analyzing their unit structure. On the other hand, unveiling the nature of the physical properties of glass has long been a big challenge in physics due to the intrinsic randomness of its structure. Additionally, understanding the properties of glass requires extracting hidden governing laws from seemingly random information, making glass an attractive simplified model for various complex mathematical problems.
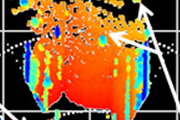
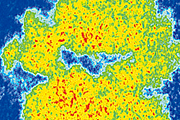
In this study, we analyzed the plastic deformation of glasses employing large-scale molecular simulations. When the load applied to a glass sample exceeds a certain level, the sample experiences catastrophic destruction. Although this remarkable phenomenon has been understood as an example of a ‘critical phenomenon*,’ our analyses revealed that the plasticity of glasses has a peculiar feature that is not common to other critical phenomena. The results of this study not only help in understanding the behavior of various materials but also provide potential clues for making machine learning more interpretable.
* Critical phenomena refer to the singular behaviors observed in many systems, characterized by features such as the ‘existence of a single length scale that governs the whole phenomenon’ and ‘universality, where the behavior does not depend on the specific details of the system, such as whether the components are spins or molecules.’
Title: Scale Separation of Shear-induced Criticality in Glasses
Authors: Oyama, N., Kawasaki, T., Kim, K., Mizuno, H.
Journal Name: Physical Review Letters
Published: April 3, 2024
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.132.148201